Ozone is a gas consisting of three oxygen molecules, its unstable electrons make it a strong oxidizing agent that can kill bacteria, viruses, fungi and other toxins. In commercial networks, ozone technology in food processing is used to purify food and water, to support the breakdown of toxic waste, to disinfect surfaces in the pharmaceutical sector and to preserve food stored in the food industry.
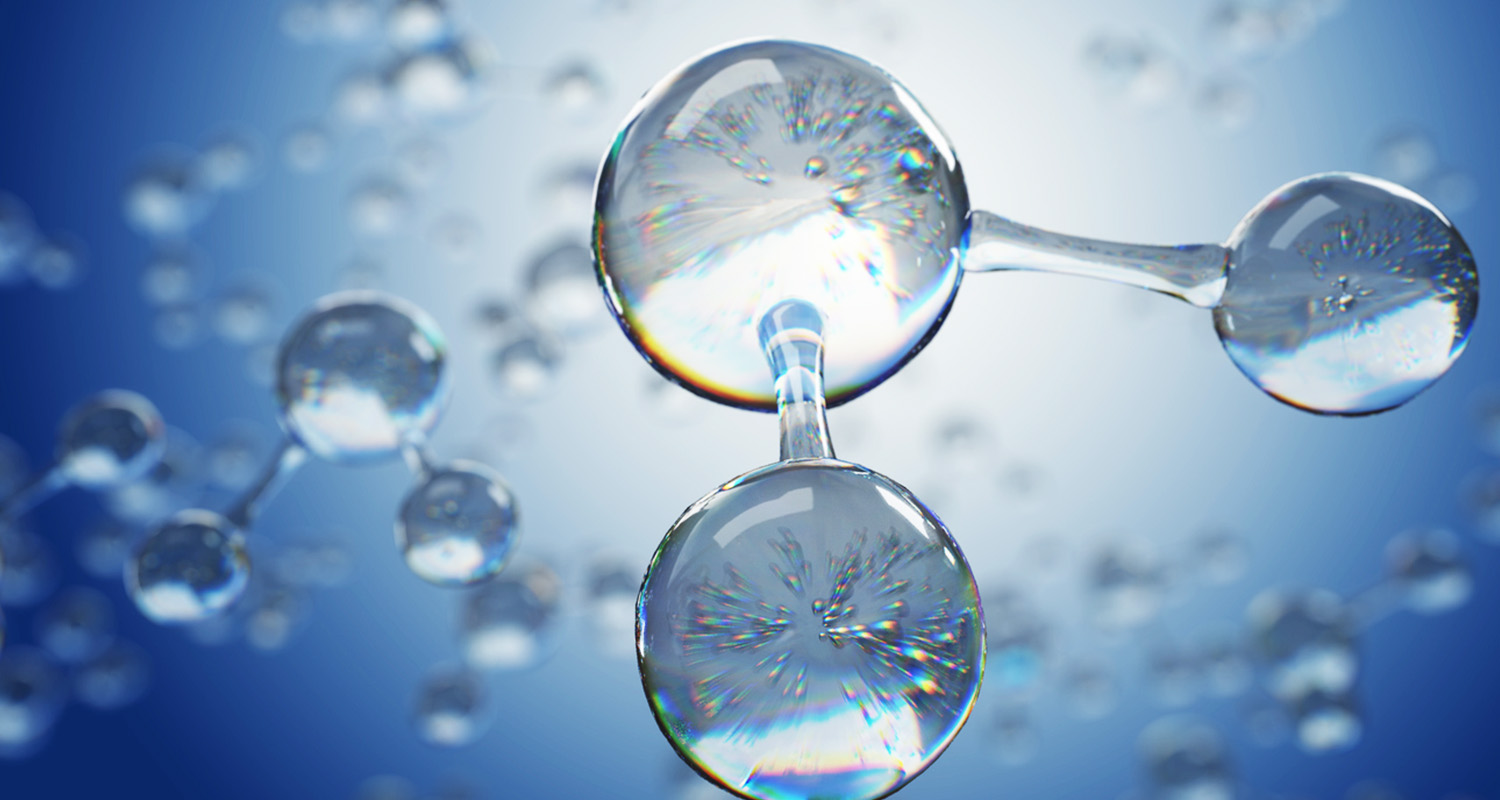

Image Source Google
The history of the use of ozone in medicine dates back to the early 1900s when Dr. Joachim Hansler invented the first reliable ozone machine. Ozone was then successfully used during World War I to treat German soldiers suffering from gangrene due to an infection that thrived in an oxygen-free environment. Ozone exposure, which involves placing the affected limb in an airtight bag and filling it with ozone, helps kill harmful bacteria.
Ozone can also be given by colon insufflation. With colon insufflation, ozone reaches the liver plexus and can be used not only to treat colon diseases, but also to enhance liver detoxification. Another effective method of using ozone is mild automatic chemotherapy. This includes drawing small amounts of blood, ozonation, and injection into the muscle. It stimulates the immune system, especially the second line of defense, and helps eliminate chronic viruses, inflammation, and other foreign substances from the body.
Ozone also increases the efficiency of the body's antioxidant system by helping to eliminate excess free radicals, which are known to cause many degenerative diseases. Perhaps the most powerful effect of ozone is to strengthen the immune system. By stimulating the production of white blood cells and releasing immune messenger substances called cytokines, ozone helps the body fight many infections and inhibits tumor growth.