Music is a universal language that has the power to evoke emotions, trigger memories, and connect people across cultures and boundaries. But have you ever stopped to think about the science behind music? How do acoustic tests shape our sonic experience and influence the way we perceive and enjoy music?
Acoustic tests play a crucial role in understanding how sound travels, how it interacts with different materials and surfaces, and how it is perceived by the human ear. Through a series of experiments and measurements, scientists and audio engineers are able to study the intricate relationships between sound waves, frequencies, and amplitude, and how they contribute to the overall listening experience.
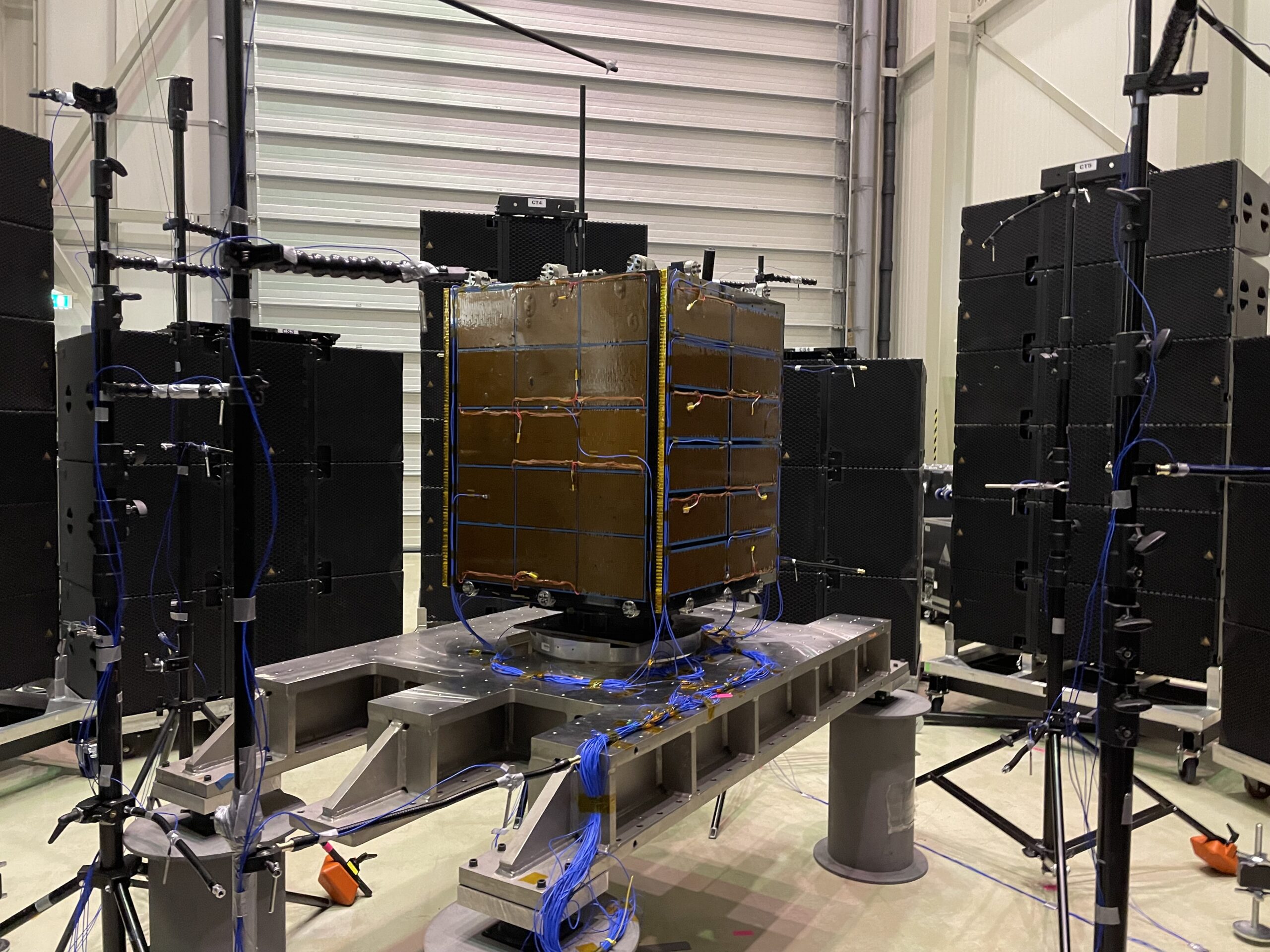
One of the key aspects of acoustic testing is the study of room acoustics. The shape, size, and materials of a room can significantly impact the way sound behaves within it. For example, a small, carpeted room will absorb more sound and create a warmer, more intimate listening environment, while a large, bare room will reflect sound and create a more spacious, reverberant atmosphere. By using specialized tools such as microphones, speakers, and sound level meters, researchers can measure the acoustic properties of a room and make adjustments to optimize the listening experience.
Another important area of acoustic testing is the study of sound reproduction systems, such as speakers and headphones. These devices play a critical role in how we experience music, as they convert electrical signals into sound waves that reach our ears. Through a series of tests, scientists can assess the frequency response, distortion levels, and spatial imaging capabilities of different audio systems to determine their overall sound quality and fidelity.
One commonly used test in evaluating audio equipment is the frequency response test. This test measures how accurately a device reproduces different frequencies across the audible spectrum, from low bass tones to high treble tones. A flat frequency response curve indicates that the device is reproducing all frequencies evenly, without emphasizing or de-emphasizing any particular range. This is important for achieving a natural, balanced sound that accurately reflects the original recording.
In addition to frequency response, acoustic tests also focus on distortion levels. Distortion occurs when a device introduces unwanted artifacts or changes to the original sound signal, leading to a loss of clarity and detail. By measuring distortion levels at different volume levels and frequencies, researchers can identify any issues and make adjustments to improve the overall sound quality of the audio system.
Spatial imaging is another important aspect of acoustic testing. This refers to the ability of an audio system to create a sense of space and dimensionality in the soundstage, allowing listeners to pinpoint the location of different instruments and voices within the mix. Through specialized tests such as binaural recordings and impulse response measurements, researchers can assess the spatial imaging capabilities of audio systems and make adjustments to enhance the listener's sense of immersion and realism.
Overall, acoustic testing plays a vital role in shaping our sonic experience and influencing the way we perceive and enjoy music. By studying the intricate relationships between sound waves, frequencies, and amplitude, researchers can optimize the acoustic properties of rooms, evaluate the performance of audio equipment, and enhance the overall listening experience for music enthusiasts around the world.
Next time you find yourself lost in a favorite song or attending a live concert, take a moment to appreciate the science behind the music. The acoustic tests and experiments conducted by researchers and audio engineers have played a crucial role in shaping the way we experience and interact with sound, allowing us to enjoy the beauty and power of music in all its glory.